Acute prostatitis is an acute inflammation of the prostate gland caused by an infection.In the disease, swelling of the prostate is formed and purulent foci appear in its tissues.Statistical data give us the right to say that acute prostatitis in men is a common disease;with advancing age, the risk of its occurrence increases.
The effectiveness of the treatment of acute prostatitis directly depends on the timeliness of the patient's treatment.The disease quickly turns into a chronic form, the treatment of which is longer and more complicated.
Forms of acute prostatitis
If we talk about the clinical development of acute prostatitis in men, there are three forms (stages) of the disease:
- catarrhal;
- follicular;
- parenchyma.
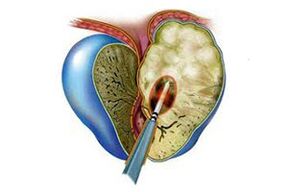
First, the catarrhal inflammation appears, which is characterized by the expansion of the acini and the appearance of reactive edema of the interstitial tissue.This leads to a significant enlargement of the prostate gland.The next stage is the rapid spread of inflammatory processes in the lobules and excretory ducts of the prostate.We are talking specifically about the excretory ducts of the prostate glands leading to the back of the urethra.Inflammatory changes affect only the mucous membranes.The excretory ducts lose their contractility, they narrow significantly or become completely blocked, creating obstacles to the release of prostatic secretions.The catarrhal form is directly related to the infectious pathogen that has moved from the back of the urethra.Since the inflammatory process also affects prostatic secretion, it can provoke the appearance of posterior urethritis.
During the follicular stage, foci of inflammation reach and spread to individual lobules or to the entire prostate gland.Purulent foci appear, pus passes into the urethra.Prostate enlargement does not stop;tissues undergo destructive changes.
During the parenchymal phase of acute prostatitis, inflammatory processes affect the interstitial tissue of the prostate gland.This stage occurs after penetration of an infectious pathogen by contact or hematogenous route, for example after surgery.
Parenchymal prostatitis at the beginning of the disease is accompanied by the appearance of single pustules, which in the process of development are united and combined with an abscess of the prostate.
As for follicular and parenchymal forms, during their development, inflammatory changes often occur in the back of the urethra and bladder neck.
Prognosis and prevention of acute prostatitis
In the majority of cases, etiotropic therapy carried out on time can eliminate the signs of acute prostatitis.If treatment is not carried out, it is quite possible that an abscess will appear or the disease will become chronic.
Prevention of this disease usually means timely treatment of any infectious diseases in the body, as well as identification and treatment of sexually transmitted diseases and urethritis.One should lead a healthy lifestyle, especially paying attention to increasing physical activity.Also, the development of the disease is prevented by regular sexual life and the absence of unprotected casual contacts.Strict compliance with the rules of personal hygiene is another important requirement for a man of any age.
Causes of the disease
Acute prostatitis in men can occur at any age.The reason is often the penetration of various infectious pathogens.This is E. coli, but there can also be streptococci, staphylococci, Candida fungi, chlamydia, trichomonas.The most common route of entry is the excretory canals.The pathogen can penetrate the prostate gland and from the bladder, which is subject to an inflammatory process (for example, acute cystitis).The infection can also spread from purulent foci located in the immediate vicinity.
The inflammatory process in the prostate caused by the presence of microorganisms can occur for various reasons.Factors that increase the risk include:
- surgical interventions in the area of the urethra;
- unprotected intercourse, inflammatory diseases of the genitourinary system in a partner;
- use of a urethral catheter;
- prostate stones etc.
The onset of acute prostatitis may not be associated with infections.It can occur as a result of a sedentary lifestyle, hypothermia and various disorders leading to stagnation in the pelvic area.
Symptoms of acute prostatitis
Since there are different stages of acute prostatitis, the symptoms of the disease often depend on them.But there are common features that unite all forms.First of all, it is pain, general intoxication, as well as problems with the urination process.
The catarrhal form is usually accompanied by severe pain, a feeling of heaviness in the perineal area, frequent urination accompanied by painful sensations.During palpation, the doctor may notice an increase in the size of the prostate gland.Secretion test results may show a high level of white blood cells.
The symptoms of acute prostatitis in the follicular form are more pronounced.A person feels pain in the perineum, radiating to the sacrum or penis.The process of urination is accompanied by pain, urine is retained, often there are difficulties with defecation.There is a general malaise and the patient has a fever.Palpation shows an enlarged prostate, its outlines become asymmetrical.Focal pain may occur.Analyzes show an increase in the level of leukocytes and the presence of purulent threads in the urine.
The parenchymal form is accompanied by a sharp rise in body temperature, the values can reach 39.5 degrees.General symptoms are expressed: chills, loss of appetite and lack of strength.Urination is delayed, the process is accompanied by severe pain.Defecation is also difficult, and constipation becomes severe.
In such cases, it is necessary to urgently start treatment of acute prostatitis.If the process begins, there is a high probability of prostate abscess, paraprostatitis, phlebitis of the paraprostatic venous plexus.If the patient does not go to the doctor, the disease becomes chronic and the probability of full recovery decreases significantly.
Diagnosis of acute prostatitis
When the patient contacts a urologist, the doctor diagnoses acute prostatitis by identifying the stage of the disease.The specialist receives the information after conducting a comprehensive study.The methods used for diagnosis in this case consist of physical, instrumental and laboratory tests.
The physical examination consists of examining the state of the prostate gland from the rectum.In this way, the specialist gets an opportunity to assess the size, shape, consistency of the organ and the presence of pain.As a result of an analysis of the secreted secretion, it is easy to determine the decrease in the number of lecithin grains and the increase in the level of leukocytes.
Palpation of the gland also includes the collection and transmission of urine for examination.In most cases, acute prostatitis is manifested by an increase in the level of leukocytes.Urine culture, PCR and blood culture, as well as analysis of urethral discharge are also prescribed.
Instrumental methods in this disease are presented by transrectal ultrasound diagnostics.If the patient has severe pain, the choice of examination is the transabdominal method.
When the question of surgical intervention arises, it is necessary to perform CT and MRI of the pelvis.
Treatment of acute prostatitis
Treatment of acute prostatitis is carried out in hospital conditions.This is due to two factors.First, there is a risk of serious complications that can affect men's health and subsequently affect reproductive function and erection quality.Secondly, the disease is complex, accompanied by pronounced symptoms and painful sensations.Treatment of acute prostatitis begins with drug therapy, and the patient is prescribed etiotropic drugs.The most important role is played by antibacterial agents, which suppress the functioning of microorganisms.
To reduce the severity of pain, as well as to get rid of spasms, the patient is recommended to take antispasmodics and analgesics.Sometimes thermal enemas and rectal suppositories are used to relieve the condition.After overcoming the acute symptoms, it becomes possible to use physiotherapy.These procedures improve microcirculation, improve local immunity and help eliminate inflammation.Among the physiotherapeutic methods for the treatment of acute prostatitis, the most effective are prostate massage, as well as microwave therapy and electrophoresis.For many years, prostate massage has been considered a particularly popular measure that helps remove congestion;it is also recommended to be used regularly as a preventive measure for men who have reached the age of forty.
A catheter is not used for problems with the urinary process;trocar cystostomy is preferred instead.
Recovery is considered the regeneration of the prostate tissue, the complete restoration of its functions, until laboratory tests show that infectious pathogens are absent and the prostate secretion returns to its normal composition.
Surgery is not a widely used treatment for prostatitis.It doesn't always work.The surgical solution brings positive dynamics in less than half of the cases.The most common side effect of the operation is erectile dysfunction, retrograde ejaculation is also common, in which during ejaculation the sperm enters the bladder, and sometimes there is a narrowing of the ureter.The surgical method does not guarantee against recurrence.Therefore, surgical intervention is resorted to only in certain cases, such as:
- the appearance of an abscess of the prostate, which must be opened and cleaned;
- lack of results from treatment with conservative methods in the form of drugs, traditional medicine, physiotherapy procedures;
- development of serious complications;
- the presence of a focus of inflammation in the pelvis;
- formation of paraproctitis (purulent abscess in cells located around the rectum);
- presence of blood in the urine;
- delayed urination and cessation of urination (anuria);
- the presence of stones in the bladder, kidneys, the cause of which is prostatitis;
- suspected malignant tumor.